In the sector of finance, specific systems are used to structure loans and investments. One machine that has gained recognition in lots of Muslim-majority nations is Islamic finance, which operates below the principles of Sharia law. A core guiding principle of Islamic finance is the prohibition of charging interest on loans, or riba. This significantly modifications the manner loans and payments are dependent. In vicinity of interest, Islamic finance makes use of methods like income-sharing, leasing, and asset-sponsored financing to make certain fairness and compliance with Sharia ideas. In this newsletter, we’ll dive into the concept of Islamic amortization, the way it works, and the key techniques used in Islamic finance.
Contents
What is Islamic Amortization?
Amortization normally refers to the process of repaying a debt through the years through regular bills. In traditional finance, these payments normally cover each the fundamental quantity and the hobby charged on the tremendous stability. However, in Islamic finance, the charging of hobby isn’t authorised. This is wherein Islamic amortization comes in.
Islamic amortization refers to repaying a mortgage in a way that aligns with Sharia regulation. Rather than paying hobby at the loan, the repayment shape is based totally on income-sharing, leasing, or different permissible techniques. This ensures that the mortgage remains freed from interest and complies with Islamic teachings. The aim is to create a honest and balanced arrangement wherein each the borrower and the lender share the dangers and rewards of the investment.
Core Principles of Islamic Finance
To better apprehend how Islamic amortization works, it’s vital to first discover the foundational principles of Islamic finance:
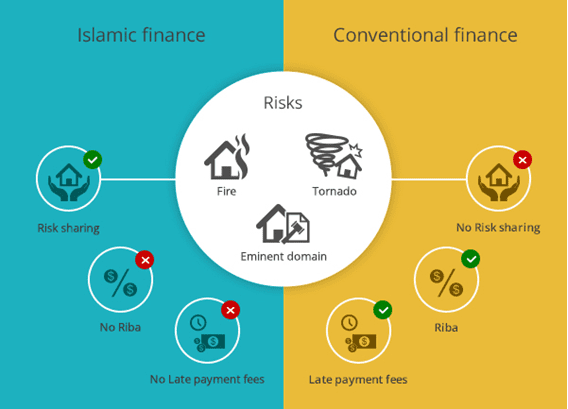
- Prohibition of Riba (Interest): Islamic finance forbids the charging of hobby, as it is visible as exploitative. The aim is to avoid unfair gains for the lender with out bearing any chance.
- Profit and Loss Sharing: Instead of hobby, Islamic finance emphasizes profit and loss sharing. Both parties—borrower and lender—proportion within the risks and rewards of the funding or financing association.
- Asset-Backed Transactions: All transactions in Islamic finance ought to be backed through tangible belongings. This ensures that the financing is tied to actual financial hobby, as opposed to speculative or debt-based practices.
- Ethical Investments: Islamic finance encourages investments in ethical industries and prohibits investment for activities like gambling, alcohol, or tobacco, which might be considered dangerous.
Islamic Amortization Methods
Several methods are used in Islamic finance to shape amortization with out charging hobby. The most common of these strategies are:
1. Murabaha (Cost-Plus Financing)
Murabaha is a extensively used technique in Islamic finance, specifically for financing purchases like houses, automobiles, or gadget. In a Murabaha agreement, the lender buys an asset on behalf of the borrower and then sells it to them at a marked-up charge. The markup represents the income the lender earns, and the price is agreed upon at the time of the settlement.
Unlike conventional loans, where the borrower pays interest on the amount borrowed, in Murabaha, the repayment is structured into constant installments. The borrower repays the loan over time, however the bills are based totally at the agreed-upon fee for the asset, in preference to any hobby on the loan stability. The borrower knows the exact quantity to pay upfront, which facilitates take away uncertainty.
While the repayment structure in Murabaha can resemble conventional amortization, it avoids hobby and ensures compliance with Islamic law.
2. Ijara (Leasing)
Ijara is any other popular Islamic financing approach that is much like leasing. Under an Ijara settlement, the lender (commonly a monetary institution) buys an asset and rentals it to the borrower for a set time period. The borrower makes ordinary condominium payments to the lender, and on the stop of the hire duration, they will have the choice to purchase the asset.
In phrases of amortization, the borrower’s bills underneath Ijara are taken into consideration apartment payments, no longer hobby payments. The quantity of each installment depends at the phrases of the rent settlement, but it does not encompass hobby fees. At the cease of the lease term, the borrower has the option to buy the asset, and the hire bills may be based to reflect this.
Ijara is commonly used for financing property like motors, property, or machinery. This structure permits the borrower to use the asset while step by step paying off the value thru lease bills.
3. Mudarabah (Profit-Sharing Partnership)
Mudarabah is a profit-sharing agreement wherein one birthday celebration affords the capital (the lender) and the alternative offers the knowledge and management (the borrower). The earnings generated from the funding are shared among the parties primarily based on a pre-agreed ratio. If the business or investment incurs a loss, the lender bears the loss, besides in cases in which the borrower is found to be negligent.
In the context of amortization, Mudarabah doesn’t involve constant repayments like conventional loans. Instead, the borrower shares within the profits of the funding. The lender receives a return based on the achievement of the enterprise or challenge. This method emphasizes equity, as both events are equally invested within the final results of the venture.
Mudarabah is commonly used for business ventures, instead of private loans. However, it still follows the ideas of danger-sharing and equity which might be vital to Islamic finance.
4. Musharakah (Joint Venture Partnership)
Musharakah is a partnership where both events contribute capital to a commercial enterprise project and proportion inside the earnings and losses in line with their respective contributions. This method is similar to equity financing in conventional finance.
In a Musharakah settlement, the borrower and lender share possession of the asset or commercial enterprise mission. Over time, the borrower can also step by step buy out the lender’s proportion, which could resemble amortization. However, not like traditional loans, the borrower and lender share both the risks and the rewards of the investment, making sure a extra equitable association.
Musharakah is usually used for actual property tasks, joint business ventures, and other massive investments. Like Mudarabah, it emphasizes risk-sharing and profit-sharing, as opposed to relying on constant payments or hobby.
Islamic Amortization vs. Conventional Amortization
The key distinction among Islamic and traditional amortization is the absence of interest in Islamic finance. In traditional finance, amortization involves fixed bills that consist of each the fundamental and the interest at the loan. The hobby is charged on the superb mortgage balance, which increases the entire quantity the borrower have to pay off.
In Islamic amortization, hobby is not charged. Instead, the repayment structure is based on earnings-sharing, leasing, or other permissible methods. This ensures that the transaction remains in line with Islamic principles, which restrict riba (hobby).
While traditional loans can be rigid and burdensome for borrowers, Islamic amortization methods are designed to be more bendy and equitable, growing a fairer financial machine.
Benefits of Islamic Amortization
- Fairness and Equity: Islamic amortization guarantees that each the borrower and lender share in the dangers and rewards of the investment. This creates a more balanced and simply financial association.
- No Exploitation: By avoiding interest, Islamic amortization prevents the exploitation of debtors, as they are now not careworn with collecting interest through the years.
- Real Economic Activity: Islamic finance requires that all transactions be sponsored by using tangible property. This reduces hypothesis and guarantees that financing is connected to actual-world economic interest.
- Ethical and Socially Responsible: Islamic finance promotes investments that align with ethical values, ensuring that budget are not used for dangerous activities inclusive of playing, alcohol, or tobacco.
Conclusion
Islamic amortization offers a unique and moral method to financing that is rooted in equity, equity, and shared responsibility. By keeping off interest and counting on earnings-sharing, leasing, and different permissible methods, Islamic finance affords a possible opportunity to standard monetary structures. Whether for personal loans, business ventures, or investments, Islamic amortization ensures that both the borrower and lender are handled fairly and that the monetary arrangement aligns with Islamic values.
If you’re thinking about accomplishing Sharia-compliant finance, knowledge Islamic amortization is important. By embracing those standards, you may participate in a greater moral and socially responsible economic gadget.